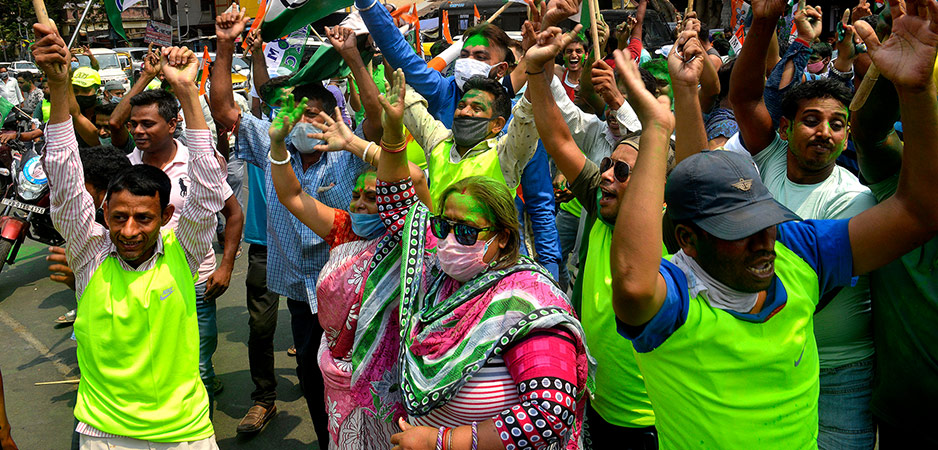In early May, the eastern Indian state of West Bengal went to the polls. The state elections attracted global attention. The BBC’s analysis of the election was headlined, “West Bengal Election: Modi Loses a Battle in the ‘War for Indian Democracy.’”
Such attention to a state election is surprising. West Bengal is not the richest, the largest or the most populous state in India. Yet it has always been an important part of the country. The British started the colonization of the Indian subcontinent by winning the Battle of Plassey in 1757. Calcutta, or Kolkata as it is now called, was the capital of British India for more than a century. Of course, West Bengal did not exist then. Bengal was the name of the British province and included modern-day Bangladesh, Bihar and Orissa then.
History Matters
It was Bengali intellectuals such as Raja Rammohan Roy, Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Swami Vivekananda and Rabindranath Tagore who led the first Indian cultural renaissance. The founder of the Bharatiya Jan Sangh, the forerunner of the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), was Syama Prasad Mukherjee, a Bengali. Manabendra Nath Roy, the founding father of Indian communism and the founder of the Mexican Communist Party, was Bengali too. So was Subhas Chandra Bose, India’s iconic freedom fighter who defeated Mahatma Gandhi’s candidate, in the party elections of the Indian National Congress.
India Is Slowly Evolving Into a Market Economy
Suffice to say, Bengal has played a larger than life role in the political and cultural life in modern India. Yet it is important to remember that this region has always sung to its own tune. Whenever a Delhi-based empire weakened, Bengal was the first province to sound the bugle of independence. Since independence, West Bengal has continued this timeworn tradition. Iconic chief ministers of West Bengal, such as Bidhan Chandra Roy and Siddhartha Shankar Ray, dealt with powerful Indian prime ministers such as Jawaharlal Nehru and his daughter Indira Gandhi as equals.
The first sustained challenge to the Congress party came from West Bengal. It was here that the communists won a historic electoral victory in 1977 and remained in power until 2011. Bengal has thrived on an us-versus-them mindset vis-à-vis the national capital, New Delhi. Bengalis believe they have been wronged by New Delhi and have to retain their independence from India’s overbearing capital. In this narrative, West Bengal is the last bastion standing against the invaders from the north, and this is the essence of Bengali pride.
Mamata Banerjee overthrew the longstanding communist government in 2011 and has been in power since. She is a feisty leader whom her admirers call “Didi,” a Bangla word for elder sister. This spinster in Kolkata has taken on the bachelor in New Delhi and won. Fittingly, a meme doing the rounds on social media adapts Asterix to Indian political lore: “One small state of Ben-Gaul still holds out against the invaders. And life is not easy for the Gow-Man believers who make the camps of Fascism, Hindutvam and Religious Extrememum…” Other variants spoke about Ben-Gaul holding out against the all-conquering North Indian invaders and their emperor, “Modius.”
How Ben-Gaul Knocked out the BJP?
Before the election, many deemed Banerjee’s victory in West Bengal unlikely. Two BJP members of parliament confidently told one of these authors that their party was headed to a victory. Banerjee’s All India Trinamool Congress, abbreviated as TMC, was facing local anger. Many accused the TMC of “misgovernance — including corruption, nepotism and high-handedness— seemed” to have put the party in peril. The BJP was promising Bengalis rapid industrialization and high growth after years of economic stagnation.
Banerjee’s right-hand man, Suvendu Adhikari, decamped to the BJP, as did many other key party members. In fact, Adhikari went on to defeat Banerjee in Nandigram, her own constituency. When the dust settles, it is clear that the BJP had reasons to be confident. Yet India’s ruling party led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi was stung by Didi’s ferocious counterpunching and was eventually knocked out. What happened?
First, the BJP did not announce a local chief ministerial candidate. It did not promote any “son-of-the-soil Bengali leader” and even mighty Adhikari was left to play a supporting role to Modi. In India’s largest state of Uttar Pradesh (UP), this strategy had worked. In West Bengal, the strategy backfired. The mother of one of the authors grew up in Kolkata and presciently remarked that Modi’s speeches in Hindi would not go down well among a people with immense linguistic pride. Modi did not even use an interpreter to translate his speeches into Bangla. Banerjee portrayed herself as the local Didi and slammed the BJP as outsiders insulting Bengali pride and even identity. It turns out that her narrative resonated with the voters.
Second, the local BJP leaders acted sycophantically. This was not in keeping with the Bengali traditions of local leaders acting as equals of leaders in New Delhi. Bengalis feared that the BJP would reduce West Bengal into vassal status. The historic suspicion of Gujaratis and Marwaris, the trading castes who once collaborated with the British, also kicked in. Modi and his chief aide, Amit Shah, are both Gujaratis. When local leaders invoked the two national leaders repeatedly as Modiji and Amitji, they offended Bengali sensibilities and triggered old suspicions.
Third, the BJP failed to take into account the legacy of India’s first cultural renaissance. This intellectual, social and cultural movement that began in the late 18th century and continued till the early 20th century continues to shape the Bengali ethos. It challenged pernicious customs such as caste, dowry and sati, the burning of wives on their husband’s pyres. Inspired by secularist, modernist and humanist ideals, Bengali intellectuals set out to modernize not only Bengali but also Indian society. Middle-class Bengalis have long seen themselves as “bhadralok,” well-mannered persons. Modi himself constantly pays homage to Swami Vivekananda, a charismatic Bengali spiritual figure. Yet he was unable to appeal to the bhadralok legacy of West Bengal. Too many Bengalis saw Modi as peddling a revanchist version of Hinduism that they had fought hard to reform.
A case in point is the BJP’s crusade against the consumption of beef. Unlike much of India, meat eating has never been taboo in the Bengali tradition. Even saints have not ordained against eating meat or fish. West Bengal remains one of the few states where beef is freely sold. The BJP used strategies that worked elsewhere in states like UP and Bihar. The party failed to keep its finger on the unique Bengali pulse that beats to a more self-proclaimed liberal rhythm. The caste-based politics by the BJP had limited success, as did the specter of moral policing as under UP’s hardline Hindu chief minister, Yogi Adityanath.
Fourth, the BJP’s narrative of local Hindus getting subsumed by Bangladeshi Muslim immigrants failed against the TMC’s narrative of New Delhi reducing Kolkata to feudatory status. Under Banerjee, Bangladeshi immigration has increased and caused unease among many voters. Yet there is a strong linguistic and regional identity in West Bengal. The partition of 1947 has not cast such a bitter memory as in Punjab. Bangladesh itself broke away from Pakistan in 1971 on linguistic grounds. Bengali pride trumped Hindu identity at least this time around.
Fifth, Banerjee deserves much credit for campaigning with great energy and a clear message. West Bengal has done well in reducing poverty and achieving higher agricultural growth than in the rest of the country even if overall economic growth has been low. Also, Banerjee’s schemes for the rural poor and women have won her much support. Modi has won a majority of the women’s vote because of his last-mile welfare programs. Here, Banerjee won most of the women’s votes in a fundamentally matriarchal society that worships the goddesses Durga and Kali.
Finally, there is a politically incorrect point that analysts often overlook. One of the authors is Bengali and can attest that bhadralok culture has prized learning over wealth. In part, this might have been a defense mechanism to cope with the poverty the British inflicted on this part of the world. In part, this might be a reaction to the Marwari pursuit of wealth by collaborating with the British. To this day, many Bengalis distrust Gujaratis and Marwaris, whom they see as money-grubbing soulless creatures. The older generation still professes wistful love for the old multinational firms that dominated Kolkata till the 1970s such as Burn Standard, Andrew Yule and Balmer Lawrie.
Arguably, the Bengali distrust of money has led to low growth in the state. The Bengali diaspora around the world wax lyrical about the preservation of their distinctive “Bangaliyana” and how they are culturally different from the rest of India. Yet, unlike Gujaratis, very few Bengalis invest in their home state. They invest in West Bengal only when they return to retirement in Kolkata. Like many cities in Italy, Kolkata is becoming a city of geriatrics with the young leaving in droves for jobs elsewhere.
Even in 2021, Bengalis tend to be employees, not entrepreneurs. They flock to all parts of India and indeed much of the world to work as doctors, lawyers, accountants, academics, administrators and more. In the last few years, startups have taken off in India, including economic backwaters like Kerala and Odisha. Yet West Bengal still lacks any meaningful startup culture.
The BJP’s constant championing of development, industrialization and growth might have rubbed off this deep-seated suspicion of entrepreneurship, business and wealth in the Bengali psyche. It did not help that Modiji and Amitji were Gujaratis spouting Hindi in a state that is proud of its distinctness from India. As mentioned earlier, the province of Ben-Gaul has historically been the first to secede from pan-North Indian empires. No wonder Didi beat Modi.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Fair Observer’s editorial policy.
Support Fair Observer
We rely on your support for our independence, diversity and quality.
For more than 10 years, Fair Observer has been free, fair and independent. No billionaire owns us, no advertisers control us. We are a reader-supported nonprofit. Unlike many other publications, we keep our content free for readers regardless of where they live or whether they can afford to pay. We have no paywalls and no ads.
In the post-truth era of fake news, echo chambers and filter bubbles, we publish a plurality of perspectives from around the world. Anyone can publish with us, but everyone goes through a rigorous editorial process. So, you get fact-checked, well-reasoned content instead of noise.
We publish 2,500+ voices from 90+ countries. We also conduct education and training programs
on subjects ranging from digital media and journalism to writing and critical thinking. This
doesn’t come cheap. Servers, editors, trainers and web developers cost
money.
Please consider supporting us on a regular basis as a recurring donor or a
sustaining member.
Will you support FO’s journalism?
We rely on your support for our independence, diversity and quality.